Props
Also known as Traffic Variables, props are used to record the number of times a value was captured or occurred.
For example, you would use a prop report to answer the question ‘How many searches for ‘Food Processor’ have we had this week?’, or ‘How many times was the Home Event banner on the Homepage clicked?’ A prop value is counted as it happens, but is then forgotten and is not tied to any subsequent actions made by the user. You should only use traffic metrics with prop reports, such as;
- Page Views
- Visits
- Instances
- Exit Rate
- Entry Rate
- Bounce Rate
Some examples of prop reports include;
- Pages
- Site Sections
- Global Nav Interaction (prop38)
- Error Message (prop6)
eVars
Also known as Conversion Variables, eVars are used to tie success events (such as sales and orders) back to the last value that was captured before the success event occurred. You would use an eVar report to answer the question ‘How many orders did the search term ‘Food Processor’ generate this week?’, or ‘How much revenue did the Home Event banner generate?’ Once an eVar value is counted, it persists until it expires or is overwritten. The point of expiry is set by us in the Adobe console, examples include end of visit or after 7 days.
You should use conversion metrics with eVar reports, such as;
- Revenue
- Orders
- Units
- Average Order Value
- Conversion
Some examples of eVar reports include;
- Static Pages (eVar6)
- Search Term: onClick (eVar4)
- Promotion Code (eVar11)
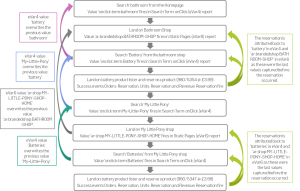
Below is an exmaple of a customer journey, and how metrics such as orders and revneue would be attributed to eVar values throughout the journey;
The below gives a summary of how the sales in the above example journey would be attributed to each eVar value;
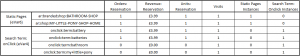
- Both pages are assigned one order, one visit and one instance. They are both assigned £3.99 of revenue (price of the products reserved).
- The terms ‘battery’ and ‘batteries’ are each assigned one order, one visit and one instance. They are both assigned £3.99 of revenue (price of the the products reserved). The terms ‘bathroom’ and ‘my little pony’, however, are only assigned a visit and an instance. They are not assigned any orders, revenue or units as their values were overwritten by ‘battery/batteries’ before the sales occurred.
Success Events
Success events are Conversion variables which capture when a desired action by a user occurs. These are then tied back to eVar values that were set before the action occurred. They are a count of the number of times the action happened so are always numerical values. Success events can also be thought of as KPI’s as they are usually actions we want to encourage customers to make. Some examples include;
- Trolley: Item Added
- Orders: Home Delivery
- Revenue: Reservation
- Trolley: Created
- Product View
- Logins
- Registrations